Get Free Demo to our Portal to Manage your Entity
or Start a Local Business.

Starting a business in Latvia offers several advantages, including a strategic location in the heart of Europe, a favorable tax regime, and a business-friendly environment. Both EU and non-EU residents can easily establish companies through services like House of Companies' Entity Management, ensuring compliance with all legal and administrative requirements. Latvia also provides tailored support for non-residents, facilitating a smooth and efficient setup process.
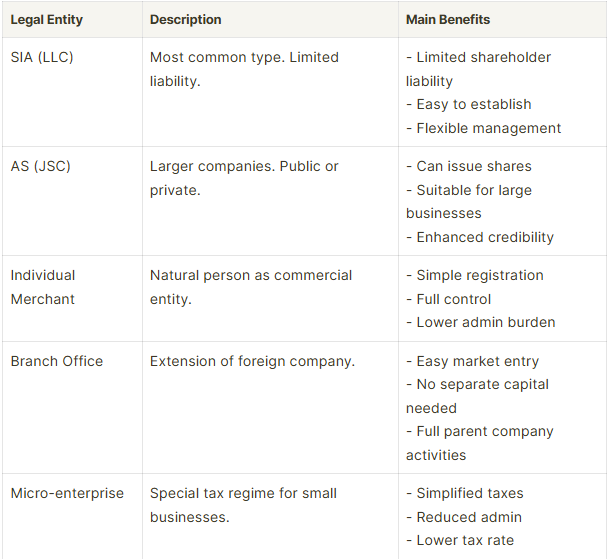
Selecting the right business structure is essential for success in Latvia. Common options include Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Limited Liability Company (SIA), and Joint Stock Company (AS). An SIA offers limited liability and operational flexibility, while an AS is ideal for larger businesses seeking to raise capital. Understanding these options allows you to choose the most suitable structure for your business objectives.
Registering a company in Latvia involves a series of essential steps and coordination with various government agencies. The Latvian Register of Enterprises (Latvijas Uzņēmumu Reģistrs) is the main authority responsible for company registration. The first step is selecting an appropriate company name and verifying its availability through the Register's online platform.
Next, you must prepare the necessary documentation, including the company's articles of association. Once your documents are ready, submit the required forms and supporting materials, along with the registration fee, to the Register of Enterprises.
Upon successful processing, you will receive your certificate of incorporation. The entire process is conducted online through the Register's e-service platform, ensuring a seamless and efficient experience for both residents and non-residents. House of Companies offers entity management services to assist you throughout this process, ensuring a hassle-free registration. For more details and to begin your registration, visit the official Latvian Register of Enterprises website.
The timeline for setting up a company in Latvia can vary depending on the complexity of your business and the completeness of your application. However, Latvia is known for its efficient and straightforward company registration process, making it an appealing destination for entrepreneurs looking to establish a business quickly. For a standard company registration, the process usually takes between 5 to 7 working days.
If you need to accelerate the process, Latvia offers an expedited registration service, allowing you to complete the setup in as little as 3 working days, subject to an additional fee. It is crucial to ensure that all required documents are accurate and complete, as any errors or missing information may cause delays.
To ensure a smooth and timely registration, it is recommended to carefully review all forms and documentation before submission. House of Companies provides expert entity management services to help streamline the registration process, ensuring your company is set up efficiently and quickly in Latvia.
When starting a business in Latvia, one of the first key decisions is choosing the right legal structure. The selection of your business entity depends on factors such as the size of your operation, tax considerations, and regulatory requirements. Common structures in Latvia include the Limited Liability Company (SIA), Joint Stock Company (AS), Sole Proprietorship, and Branch of a Foreign Company.
The Limited Liability Company (SIA) is the most popular option due to its limited liability protection, making it ideal for most businesses. Alternatively, establishing a Branch of a Foreign Company allows international entities to operate in Latvia without forming a separate legal entity. Understanding the benefits and challenges of each structure is essential to ensure it aligns with your business objectives.
House of Companies offers comprehensive entity management services to help you choose the most suitable legal structure for your business. Their expert team will guide you through the details of each option, ensuring you make an informed decision that supports your long-term success in Latvia.
Non-residents looking to establish a company in Latvia should be aware of several important considerations. First, while there is no strict requirement for a director to be a resident of the EU/EEA, the company must have a local contact person or a registered office in Latvia.
Secondly, regardless of where the directors or shareholders are based, the company must have a physical registered office address in Latvia, not just a P.O. box. This address will be used for official communications.
Third, compliance with Latvian tax laws and regulations is essential. This includes registering for taxes, submitting annual reports, and maintaining proper financial records. Lastly, although much of the business can be managed remotely, having a local presence or representative can be beneficial for day-to-day operations and ensuring ongoing compliance with local laws and regulations.
For non-residents, the most common and suitable legal entities in Latvia are the Limited Liability Company (SIA) and the Branch of a Foreign Company. The SIA offers limited liability, meaning the personal assets of shareholders are protected from the company’s debts. This structure is the most popular for most businesses and is relatively simple to establish and maintain.
The SIA also offers flexibility for future growth, allowing for the addition of shareholders or investors as needed. In contrast, a Branch of a Foreign Company enables international businesses to establish a presence in Latvia without forming a separate legal entity. This is beneficial for companies that wish to retain control from the parent company or are testing the Latvian market before establishing a fully independent entity.
While the SIA and Branch are the most commonly used structures, other entities like the Joint Stock Company (AS) may be more appropriate in specific scenarios, particularly for larger businesses seeking to raise capital or engage in more complex operations.
Registering a branch of a foreign company in Latvia involves a specific process to establish your presence while maintaining the link to the parent company. The first step is to submit the necessary application forms to the Latvian Register of Enterprises (Latvijas Uzņēmumu Reģistrs). This process requires detailed information about both the parent company and the Latvian branch.
Along with the registration forms, you must provide certified copies of the parent company’s Articles of Association (or equivalent documents) and the certificate of incorporation. These documents should be translated into Latvian or accompanied by a certified translation. You will also need to provide the details of the branch’s local representative, such as a director or a contact person for the Latvian branch.
After gathering the required documents, you must pay the registration fee. Upon successful registration, the branch will receive a unique registration number, distinct from the parent company’s number. Although the branch is not a separate legal entity, it must comply with Latvian reporting, tax, and regulatory requirements. For more detailed information on branch registration and ongoing compliance obligations, you can visit the Latvian Register of Enterprises official website.

The Articles of Association is a crucial document for a company in Latvia, as it outlines the internal governance rules and procedures that guide the company's operations. It serves as the company’s constitution, defining how it will be managed and governed. When drafting the Articles of Association in Latvia, several key elements must be addressed. Firstly, the document must clearly specify the company name and the registered office address in Latvia. This address must be a physical location where the company can receive official correspondence.
Secondly, the Articles of Association should outline the share capital structure, including the types and value of shares, and the rights of shareholders. It should specify voting rights, the procedure for transferring shares, and the powers associated with each class of shares. The document should also define the roles, powers, and responsibilities of the directors, including how they are appointed, removed, and their duties to the company. It may also outline how decisions are made at the board level.
Additionally, the document must include clear procedures for decision-making for both the board of directors and the shareholders. These procedures are essential for ensuring efficient operations and managing any conflicts. The Articles of Association should also include provisions for conflict resolution and any company-specific rules or operational guidelines necessary for smooth functioning.
Given the legal importance of the Articles of Association, it is highly advisable to consult with a legal professional to ensure that the document complies with Latvian company law. A legal expert will help ensure that the Articles provide the necessary protections for all involved parties and that the company’s internal governance is clearly defined in compliance with Latvian corporate regulations.
When appointing directors and shareholders for your Latvian company, there are several important factors to consider. While Latvia does not have a specific legal requirement that at least one director must be a resident of the country or the European Economic Area (EEA), it’s still important to have a local presence for practical reasons. There is no bond required for non-EEA directors, but the company must have a registered office in Latvia.
Along with the directors, it is important to determine the number and type of shares to issue, which will affect the company's capital structure and the rights of shareholders. Initial shareholders and their shareholdings must also be identified.
Directors in Latvia have legal duties, including acting in the best interests of the company, exercising independent judgment, and avoiding conflicts of interest. When appointing directors, it is important to consider their skills, experience, and ability to fulfill these responsibilities. While Latvia does not have a maximum number of directors, the Articles of Association can set a limit.
For Latvia, the company registration process is handled by the Register of Enterprises of the Republic of Latvia (Latvijas Uzņēmumu Reģistrs). Upon incorporation, your company is automatically registered with the Register, and it will be assigned a unique company registration number (Reģistrācijas numurs). This number is crucial for official communications, including interactions with government agencies and for tax purposes with the State Revenue Service (Valsts ieņēmumu dienests).
Responsibility for Accurate Information
While the registration with the Register of Enterprises is automatic, it is your responsibility to ensure that all information provided during the registration is accurate and current. If there are any changes, such as a modification in directors, shareholders, or the registered office address, these must be reported to the Register without delay to ensure compliance with Latvian law.
Public Accessibility of Company Information
The Register of Enterprises maintains a public record of company information, which includes the company’s name, registration number, and registered address. This transparency ensures that the company’s key details are accessible to the public, enhancing trust and facilitating business transactions.
Once your company is incorporated in Latvia, you must register for Corporation Tax with the State Revenue Service (VID). This registration is mandatory for all companies, whether or not they are actively trading. Completing this registration promptly ensures that your company complies with Latvian tax obligations from the outset.
If your company's taxable turnover is expected to exceed €40,000 in a 12-month period, you must register for Value Added Tax (VAT). However, if your turnover is below this threshold, you can choose to register voluntarily. VAT registration is crucial for tax compliance and streamlining your business finances, as it allows you to reclaim VAT on eligible expenses.
If your business plans to employ staff, you must register as an employer with the State Revenue Service (VID). This registration is required even if you are the sole employee. Registration can be done online through the VID E-services portal, ensuring that you remain compliant with Latvian payroll taxes and social security contributions.
If you plan to employ staff in your Latvian company, you must register as an employer with the State Revenue Service (VID) and comply with the Latvian payroll tax system. This process involves several important steps and ongoing responsibilities.
First, you’ll need to register as an employer with the State Revenue Service (VID). This can be done online via the VID E-services portal and should be completed before you start paying wages to any employees. Once registered, you’ll need to set up a payroll system that is capable of calculating mandatory deductions, including income tax, social security contributions, and health insurance contributions.
As an employer, you are required to calculate and deduct these amounts from your employees’ wages and remit them to the State Revenue Service (VID). Additionally, all payroll information must be submitted to the VID, including monthly declarations of tax withholdings.
Since these calculations can be complex, many employers use payroll software or outsource this function to third-party providers. It’s crucial to ensure that all payroll submissions are accurate and timely to avoid penalties. For detailed guidance on your employer obligations and how to comply with Latvia’s payroll system, you can refer to the VID Employer's Guide available on the official VID website.
Choosing the right business structure is a crucial decision that will have long-term implications for your business in Latvia. The primary options available are Sole Proprietorship, Limited Liability Company (SIA), and Partnership, each offering unique advantages and considerations.
A Sole Proprietorship is ideal for individuals running a business alone. It is the simplest to set up and manage, with minimal regulatory requirements. However, it does not provide limited liability, meaning that personal assets could be at risk if the business incurs debts.
A Limited Liability Company (SIA) is the most common structure for small and medium-sized businesses in Latvia. It provides limited liability, which protects personal assets from business debts. It is suitable for most businesses and enhances your professional reputation. However, it requires a more complex setup and ongoing compliance, including filing annual financial statements and returns.
A Partnership can be either a general partnership or a limited partnership, with each partner sharing ownership and management responsibilities. In a general partnership, all partners share liability, whereas, in a limited partnership, there is one or more partners with limited liability. This structure, like a sole proprietorship, does not offer limited liability protection unless it is a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP).
Each structure has different legal and tax implications. For example, a sole proprietor pays personal income tax on profits, whereas an SIA is subject to corporate tax. The choice of structure depends on factors such as the nature of your business, your growth plans, the level of personal liability you're comfortable with, and your tax situation. It is advisable to consult with a legal or financial professional to ensure you select the structure that best supports your business goals and future development.
Sign up by completing the form below.
The costs associated with company registration in Latvia are relatively straightforward, though there are various fees that should be taken into account. The main cost for company registration is the state fee for registering a Limited Liability Company (SIA), which typically ranges between €150 and €200, depending on the method of registration.
If you choose to register online via the Latvian Enterprise Register (Latvijas Uzņēmumu Reģistrs), the registration fee is usually reduced, providing a more cost-effective option for many businesses. Reserving a company name is also an optional step, and the fee for reserving a company name in advance is typically around €20.
Beyond registration, you might incur additional costs. Many businesses opt to hire professionals such as lawyers, accountants, or consultants for legal and financial assistance during the setup process. The fees for these services vary depending on the complexity of the business and the level of support required.
For companies that require a Latvian-resident director, there may be extra costs for nominating a director who is a resident of Latvia or the European Economic Area (EEA). Additionally, if your business operates under a trade name different from the registered company name, you will need to register the business name separately, with a typical fee of around €15.
While these expenses might seem considerable, they are a one-time investment in ensuring your business is established properly in Latvia and is compliant with local regulations.
Latvia’s tax system offers several benefits, making it an attractive destination for businesses, especially international companies and startups. One of the notable advantages is the corporate income tax rate of 20%, which is applied on the profits of companies.
However, Latvia has a unique tax system that benefits retained earnings. Companies in Latvia are not taxed on retained earnings; corporate income tax is only due when profits are distributed (e.g., through dividends or other distributions). This system encourages reinvestment into the business and helps reduce the overall tax burden for companies that choose to reinvest their profits.
Latvia has an extensive network of double taxation agreements with over 50 countries, which helps businesses avoid paying tax on the same income in different jurisdictions, a useful feature for businesses operating internationally.
Latvia also offers tax incentives for businesses engaged in research and development (R&D). Companies investing in R&D activities may benefit from tax relief and deductions, reducing their overall tax liabilities.
For foreign dividend income, Latvia’s system is advantageous, as many foreign dividends are taxed at a lower rate (such as the 0% rate for dividends received from other EU/EEA countries, subject to conditions).
Latvia’s membership in the European Union also provides businesses with access to the EU market and a skilled workforce, making it an appealing location for companies looking to expand into the EU.
This combination of low taxes on retained earnings, favorable treatment of dividends, and access to EU markets makes Latvia an attractive location for businesses seeking to expand internationally.
Entrepreneurs starting a business in Latvia can benefit from several tax incentives designed to support new ventures and foster business growth. One key advantage in Latvia is the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) system. Unlike many countries, Latvia applies a tax on profits only when they are distributed (e.g., dividends), rather than taxing profits when earned. This encourages businesses to reinvest their earnings for growth and expansion, as reinvested profits are tax-exempt.
For companies focused on research and development (R&D), Latvia offers an R&D tax incentive, allowing businesses to claim deductions for qualifying R&D expenses. This can be beneficial for innovative startups or those involved in technology development.
Latvia also has an investment incentive program, which offers certain tax benefits for foreign and local investors. However, the specifics of these incentives can depend on the type of investment and the sector in which a business operates. For instance, investment tax relief may apply to specific industries, such as manufacturing or technology, to stimulate growth and employment.
Another relevant scheme is Latvia’s Micro-enterprise Taxation System, which provides a simplified tax structure for very small businesses with fewer than 10 employees. This tax regime offers lower rates on gross income, making it easier for small businesses to operate with fewer administrative requirements.
These incentives, together with Latvia’s position in the European Union, make it an appealing destination for new businesses. Entrepreneurs should consult the official Latvian tax authority or seek professional advice to understand which incentives may apply to their specific situation and business type.
In Latvia, companies must comply with financial reporting and audit obligations to ensure transparency and accountability. These requirements vary depending on the company’s size and type, but all businesses must maintain accurate financial records.
Companies must prepare annual financial statements in accordance with Latvian Accounting Standards or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), depending on their size and type of operations. Small companies are allowed to prepare simplified financial statements under specific criteria defined by the law.
In addition to the financial statements, companies must file an annual report with the Enterprise Register of Latvia. This includes basic company information and financial data. The annual report must be filed within 12 months of the company’s financial year-end, rather than within 28 days as in Latvia.
Audit requirements are based on the company's size. Small companies are exempt from the mandatory audit if they meet at least two of the following three criteria:
However, even if a company qualifies for audit exemption, it may still choose to undergo an audit voluntarily for added transparency or credibility.

Establishing a business bank account is a critical step for managing your company’s finances in Latvia. It is required for most business entities and essential for separating personal and business transactions while ensuring transparency.
The process is governed by Latvia's Law on the Prevention of Money Laundering and Terrorism and Proliferation Financing, which mandates thorough due diligence for all new accounts to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing regulations.
Latvia’s Financial and Capital Market Commission (FCMC) oversees the banking sector, ensuring compliance with EU regulations like the Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) for secure online banking and third-party access with account holder consent.
Opening a business bank account can take several weeks, particularly for companies with non-resident directors or complex ownership structures. Banks are required to conduct comprehensive checks on beneficial owners and stakeholders to ensure compliance with Latvian AML laws.
By preparing the required documentation and understanding the regulatory framework, you can establish a strong financial foundation for your business in Latvia.
Efficient management is crucial for businesses operating in Latvia's competitive and regulated market. Latvia offers a business-friendly environment, and optimizing your company’s operations can ensure compliance and enhance productivity.
Start by registering your company with the Commercial Register of Latvia, ensuring all necessary legal documents are accurate and up to date. Latvia's laws require companies to maintain detailed accounting records and comply with the Law on Annual Financial Statements and Consolidated Financial Statements, adhering to local or international financial reporting standards.
Utilizing digital tools such as accounting software, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, or document management tools can simplify administrative tasks and ensure compliance with regulations, such as VAT filing and payroll management. Outsourcing services like tax consultation, payroll processing, or legal compliance to local professionals is a common strategy to reduce administrative overhead while adhering to Latvia's strict regulatory requirements.
Additionally, staying updated on changes to Latvia’s tax codes and employment laws is essential. Regularly review internal policies and operations to ensure alignment with the latest regulations. Latvia’s government also provides incentives, such as EU funding programs and tax benefits for businesses involved in innovation and development.
For sustained growth and success in Latvia, efficient company management combined with strategic use of local expertise is key.
Hiring personnel in Latvia is relatively straightforward, thanks to a transparent regulatory framework and access to a skilled and multilingual workforce. Here’s an overview of the process and what to consider:
Workforce Availability
Latvia has a well-educated labor market with a strong emphasis on technical skills, IT, engineering, and finance. Many professionals are fluent in multiple languages, including Latvian, English, and Russian, making the country attractive for businesses seeking skilled talent.
Employment Contracts
Employment relationships in Latvia are governed by the Labour Law. Employers are required to provide a written employment contract specifying key terms such as job responsibilities, salary, working hours, and duration. Fixed-term and indefinite contracts are common, but all must comply with local labor regulations.
Onboarding Requirements
Before hiring, employers must:
Work Permits for Foreigners
Hiring non-EU citizens requires additional steps. Employers must obtain a work permit and ensure the individual holds a valid residence permit. The process is streamlined for highly skilled professionals, with Latvia participating in the EU Blue Card program.
Recruitment Channels
Recruitment is facilitated through online job portals, recruitment agencies, and government-backed employment services. The process is efficient, and many international companies find it easy to recruit through these channels.
Labor Costs
Labor costs in Latvia are competitive compared to Western Europe, making it an attractive option for businesses. Employers are required to pay social security contributions and adhere to minimum wage laws, which are periodically updated.
Trial Periods
Latvia allows probation periods of up to three months for new employees, giving employers the opportunity to assess a candidate’s suitability before making a long-term commitment.
Depending on your business activities, you may need specific permits or licenses to operate legally in Latvia. Below are common examples tailored to Latvian regulations:
Food Business Licenses
If you are operating a food business, you must register with the Food and Veterinary Service of Latvia (Pārtikas un veterinārais dienests). This registration ensures compliance with EU food safety and hygiene regulations. Additional permits may be required for specific activities, such as food production or handling.
Alcohol Licenses
Businesses selling alcohol need a permit from the State Revenue Service of Latvia (Valsts ieņēmumu dienests, VID). Retail or wholesale alcohol sales require separate licensing, and businesses must comply with alcohol trading laws and excise duties.
Environmental Permits
Activities that impact the environment, such as manufacturing, waste management, or emissions, require permits from the State Environmental Service (Valsts vides dienests) under Latvia’s environmental protection regulations.
Professional Services Licenses
Many professional services, including legal, medical, or financial services, require specific licensing or registration. For instance, financial service providers must obtain authorization from the Financial and Capital Market Commission (FCMC).
Building and Planning Permits
If you are constructing or modifying business premises, you must obtain planning and construction permits from your local municipal authority, as per Latvia’s Construction Law (Būvniecības likums) and associated regulations.
Music and Copyright Licenses
If your business plays music, you need copyright licenses from organizations such as AKKA/LAA (Latvian Copyright and Communication Consulting Agency). These licenses ensure compliance with copyright laws for music broadcasting and public performances.
Waste Management Licenses
Businesses involved in waste collection, transportation, or treatment need waste management permits from the State Environmental Service under the Waste Management Law (Atkritumu apsaimniekošanas likums).
Data Protection Registration
While not strictly a license, businesses processing personal data may need to register with the Data State Inspectorate (Datu valsts inspekcija) to ensure compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Latvia’s data protection laws.
Obtaining the correct permits and licenses is essential for legal compliance and smooth business operations in Latvia. Each permit is tailored to specific industries and activities, ensuring adherence to national and EU-level regulations. It is advisable to consult with regulatory authorities or legal professionals to confirm the requirements applicable to your business.
In Latvia, obtaining the necessary licenses and permits is crucial for legal business operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure your business complies with Latvian regulations:
For a full list of licenses and permits required for specific industries in Latvia, consult the Latvian State and Municipal Services Portal or visit other government websites relevant to your business.
Registration: Register with Latvia’s Data State Inspectorate (Datu valsts inspekcija) if required by Latvian law, in compliance with the GDPR.
Policies & Procedures: Develop and enforce data protection policies to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
GDPR Principles: Ensure compliance with the key principles of data processing under the GDPR, including lawfulness, fairness, transparency, and others.
Data Protection Officer (DPO): Appoint a DPO if required by GDPR Article 37, depending on the nature of your data processing activities.
Ongoing Review: Regularly review and update your data protection practices to maintain compliance with the GDPR.
Security Measures: Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to secure personal data as required by GDPR Article 32.
Data Subject Rights: Establish processes to manage data subject access requests and uphold other rights under the GDPR.
When hiring personnel in Latvia, employers must comply with several key legal requirements:
Social Security Contributions: Employers must contribute approximately 24.09% of each employee's gross salary to social security, covering pensions, health insurance, and other benefits.
Income Tax Withholding: Employers are responsible for withholding personal income tax (20%) from employees’ wages and remitting it to the State Revenue Service (SRS).
Working Time and Leave: The standard workweek is 40 hours, with employees entitled to at least four weeks of paid annual leave. Overtime is paid at a higher rate.
Health and Safety: Employers must provide a safe working environment and adhere to regulations enforced by the State Labour Inspectorate.
Anti-Discrimination Laws: Hiring practices must be non-discriminatory based on age, gender, ethnicity, disability, and other protected characteristics.
Employment of Foreign Workers: Non-EU nationals need a work permit and residence permit, while EU nationals can work freely in Latvia.
Termination and Severance: Dismissal must follow legal procedures, and employees may be entitled to severance pay depending on the circumstances.
Data Protection: Employers must comply with GDPR regarding the collection, processing, and storage of employee personal data.
Employee Benefits: Employers are required to provide certain benefits, such as paid sick leave and maternity leave. Additional benefits, like bonuses, are optional.
Starting a business in Latvia offers many advantages, including a competitive tax system, access to the EU market, and a well-educated workforce. However, it’s important to navigate Latvia's legal and regulatory environment with care.
Key points to remember:
Choose Your Business Structure: Select the appropriate structure based on factors such as liability protection and tax considerations.
Compliance with Registration and Licensing: Ensure your business meets all necessary registration and licensing requirements under Latvian law.
Stay on Top of Tax Obligations: Familiarize yourself with Latvia’s tax system and keep track of filing deadlines and tax obligations.
Understand Latvian Employment Law: If you plan to hire employees, make sure you are well-versed in local labor laws and employee rights.
Seek Professional Advice: For complex legal or financial matters, consider seeking guidance from professionals who are experienced in Latvian business regulations.
Despite the initial complexity, Latvia’s pro-business environment and support for startups make it a great destination for entrepreneurs. By following these steps and consulting experts when needed, you can efficiently and compliantly establish your business in Latvia.
What are the legal forms of business in Latvia?
What is the minimum capital requirement for an SIA in Latvia?
Do I need a business address to start a company in Latvia?
Can a foreigner own a company in Latvia?
How long does it take to register a business in Latvia?
What are the tax rates in Latvia?
Do I need to hire an accountant for my business in Latvia?
Is it easy to hire employees in Latvia?
Are there any incentives for startups in Latvia?
How do I close a business in Latvia?
Stay updated with the latest news and exclusive offers. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights delivered to your inbox!